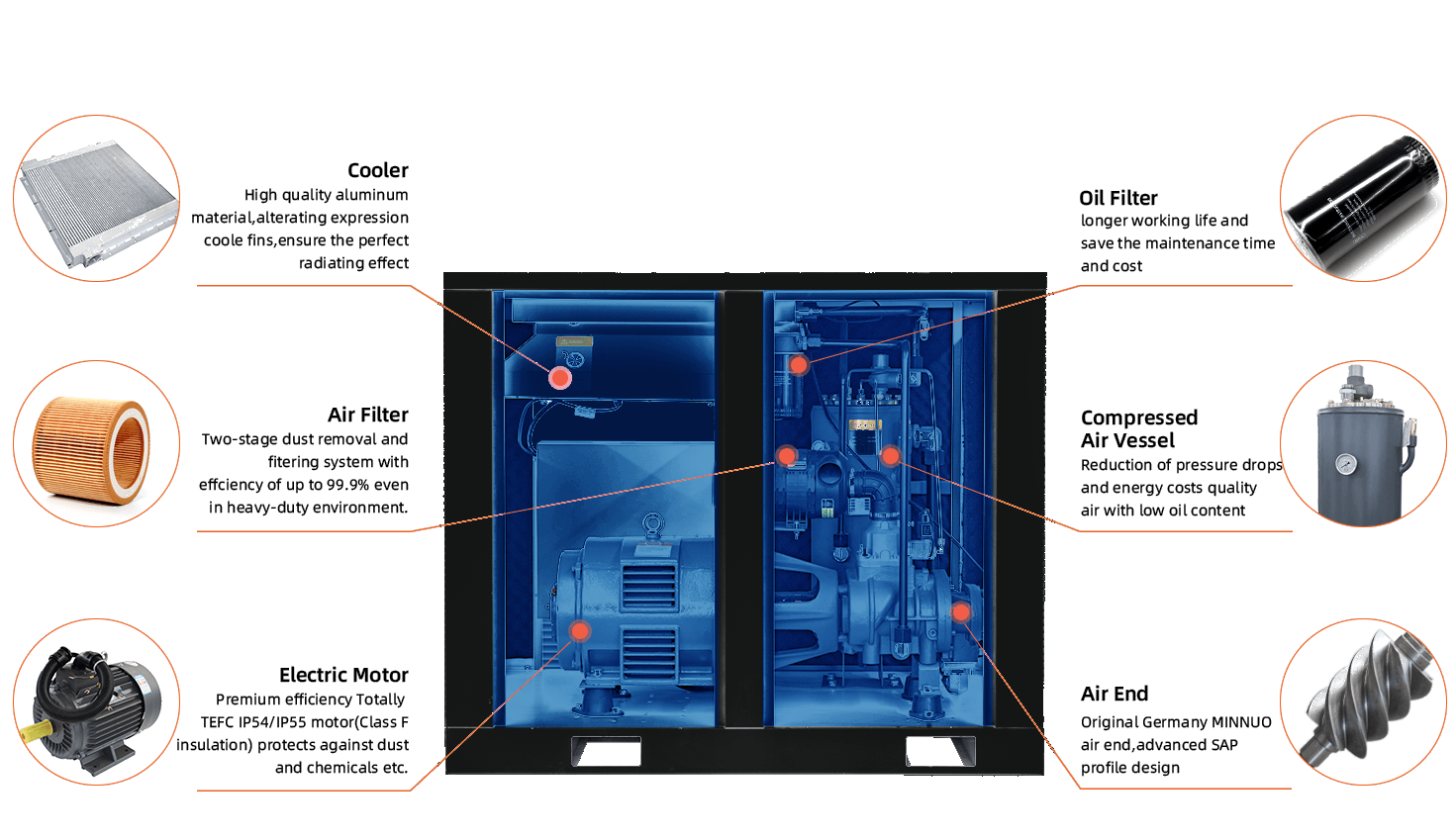
Industrial compressors are essential equipment across sectors such as energy, chemicals, metallurgy, electronics, and medical gas supply. Choosing the correct compressor type directly affects system efficiency, operational stability, and safety. This document outlines the major categories of compressors and offers a structured guide to help professionals select the most suitable one for their applications.
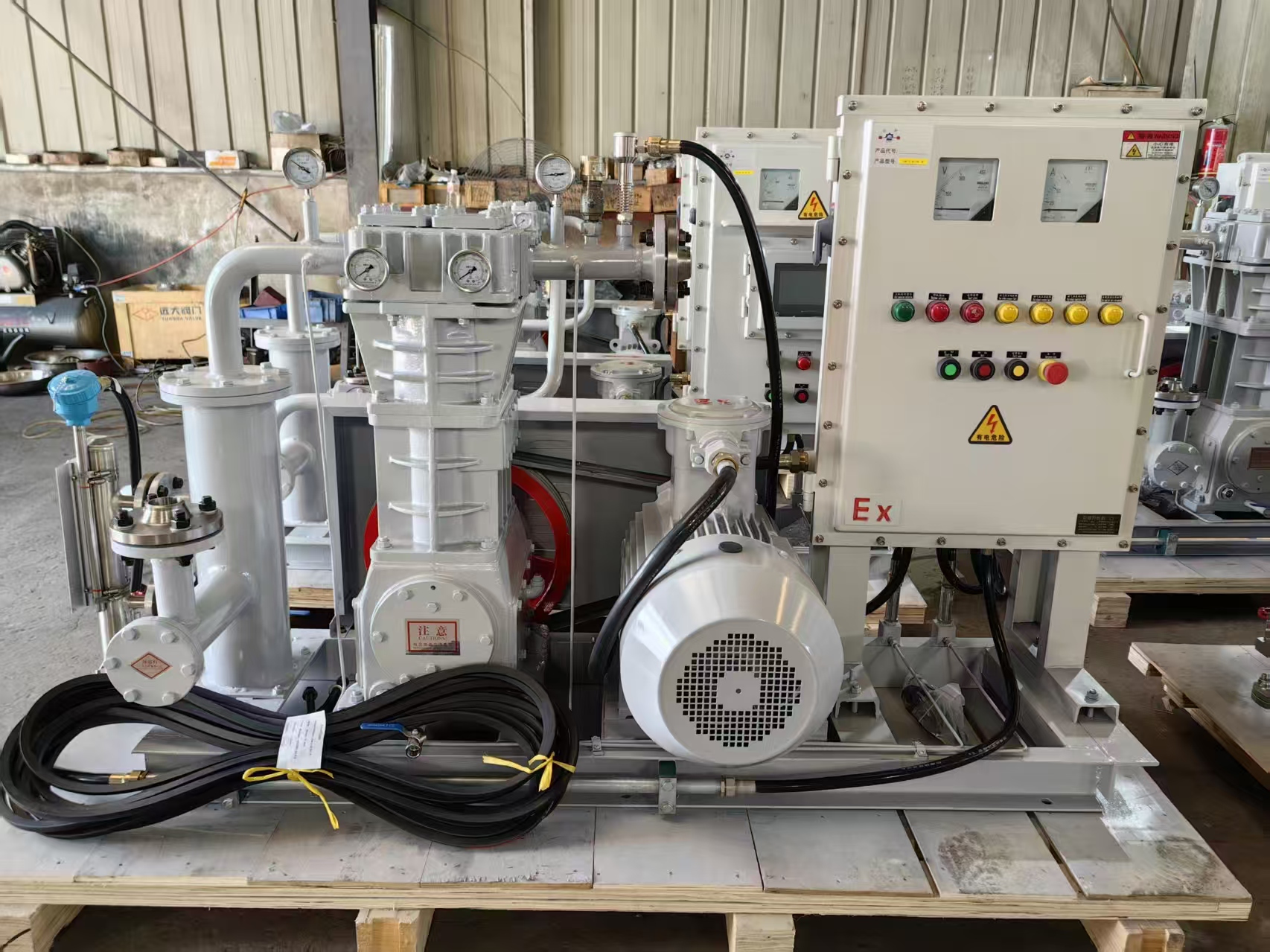
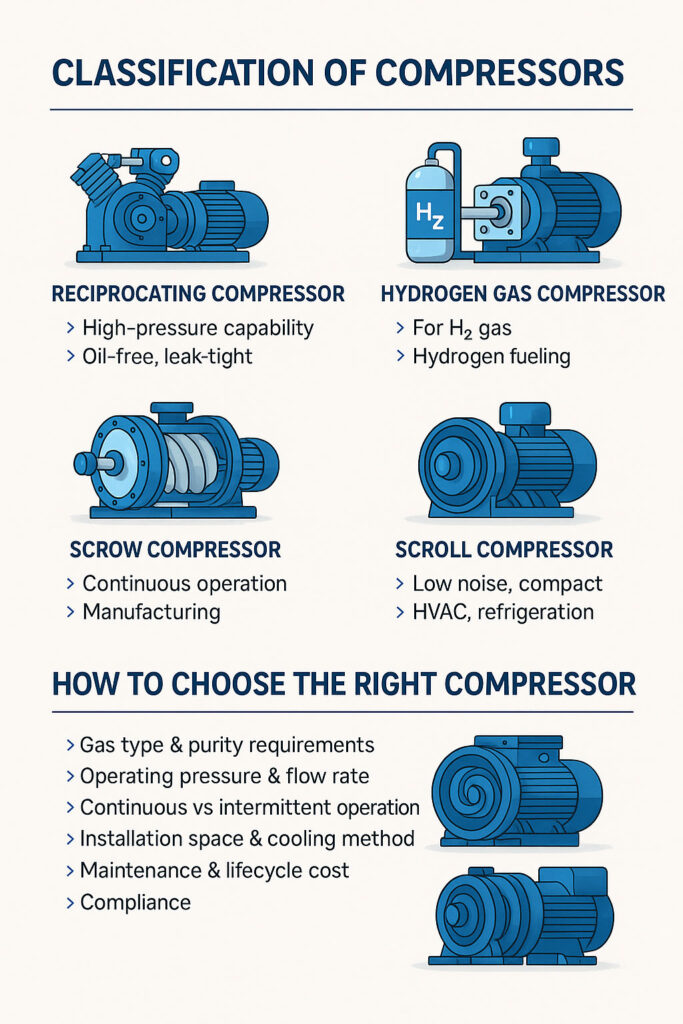
 🔧 1. Reciprocating Compressors
🔧 1. Reciprocating Compressors
Overview:
Reciprocating compressors use pistons driven by a crankshaft to deliver gas at high pressure.
Advantages:
High-pressure capability
Suitable for small to medium flow rates
Modular maintenance
Best for:
Petrochemical plants, natural gas boosting, CNG stations
💡 2. Diaphragm Compressors
Overview:
These are oil-free compressors that use a diaphragm to isolate the gas from mechanical parts.
Advantages:
Absolutely oil-free gas delivery
Ideal for high-purity and hazardous gases
Leak-tight design
Best for:
Hydrogen, oxygen, helium, and medical gas compression
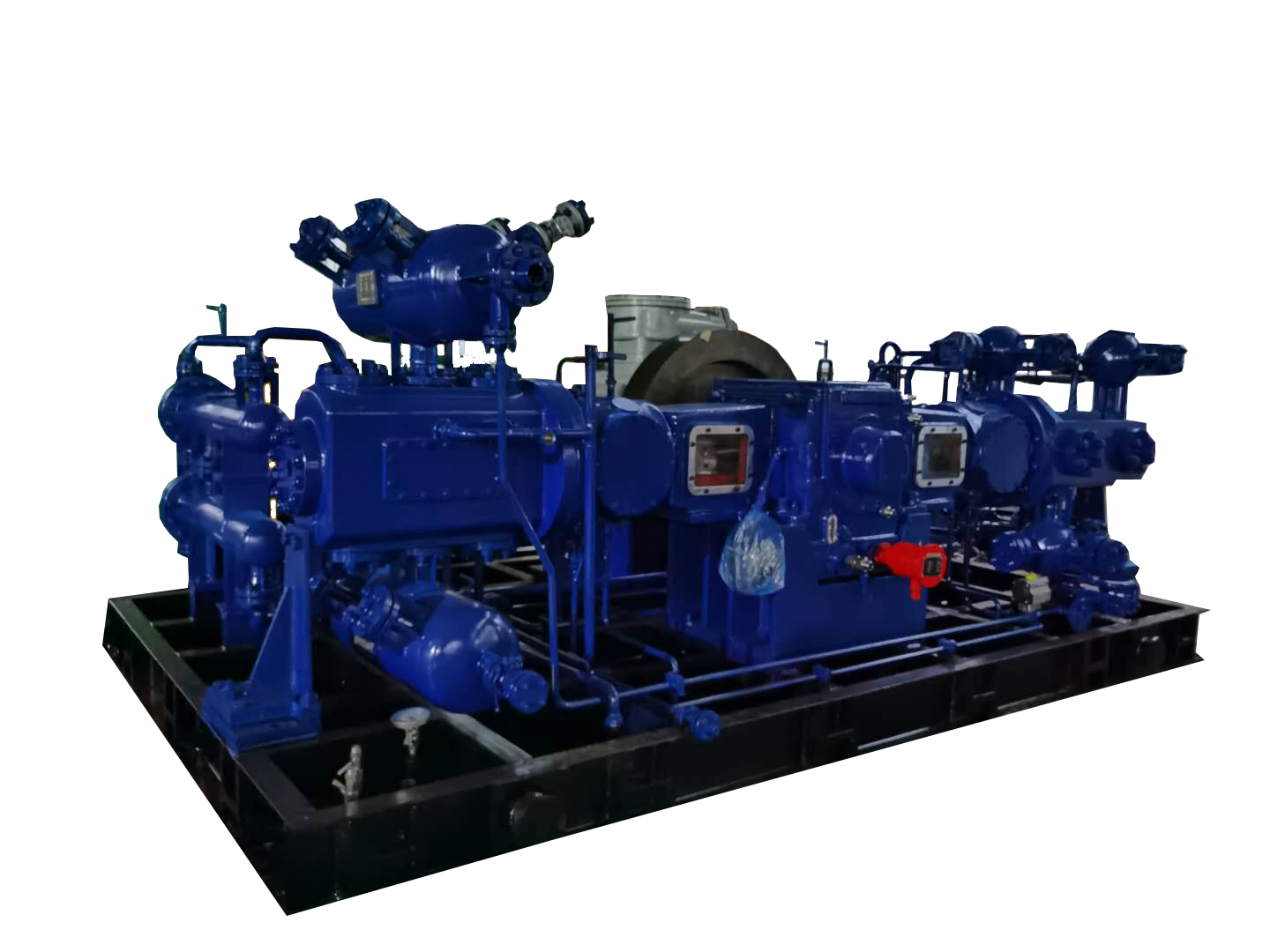
⚙️ 3. Screw Compressors (Rotary Compressors)
Overview:
Rotary screw compressors are continuous-duty machines that compress gas using two helical rotors.
Advantages:
Continuous operation
Lower vibration
High efficiency for medium pressure ranges
Best for:
Manufacturing, electronics, metallurgy, pneumatic tools
🌀 4. Scroll Compressors
Overview:
Scroll compressors use orbiting scrolls to compress gas.
Advantages:
Quiet operation
Energy-efficient
Compact footprint
Best for:
HVAC, refrigeration, laboratories
💨 5. Centrifugal Compressors
Overview:
These dynamic compressors use impellers to impart velocity to the gas and convert it into pressure.
Advantages:
High flow capacity
Fewer moving parts
Suitable for large-scale operations
Best for:
Air separation plants, LNG, chemical processes
🔬 6. Hydrogen Gas Compressors
Overview:
Specialized units designed to handle light, explosive hydrogen gas under high pressure.
Advantages:
Diaphragm or oil-free piston types preferred
High compression ratios
Excellent sealing and safety
Best for:
Hydrogen fueling stations, renewable energy storage, ammonia production
⚖️ 7. Scroll vs Screw vs Reciprocating: Quick Comparison
| Type | Pressure Range | Flow Capacity | Maintenance | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reciprocating | High | Low–Medium | Moderate | Gas pipeline, CNG |
| Diaphragm | High | Low | Low | Specialty gases, labs |
| Screw | Medium | Medium–High | Low | Industrial automation |
| Scroll | Low–Medium | Low | Low | HVAC, refrigeration |
| Centrifugal | Low–Medium | High | Low | LNG, large-scale processes |
| Hydrogen Compressors | Very High | Low–Medium | Medium–High | Hydrogen energy, clean tech |
🧭 How to Choose the Right Compressor
When selecting a compressor, consider the following factors:
Gas type & purity requirements (e.g., toxic, explosive, high-purity)
Operating pressure & flow rate
Continuous vs intermittent operation
Installation space & cooling method
Maintenance & lifecycle cost
Compliance (CE, ATEX, ISO certifications)









 🔧 1. Reciprocating Compressors
🔧 1. Reciprocating Compressors