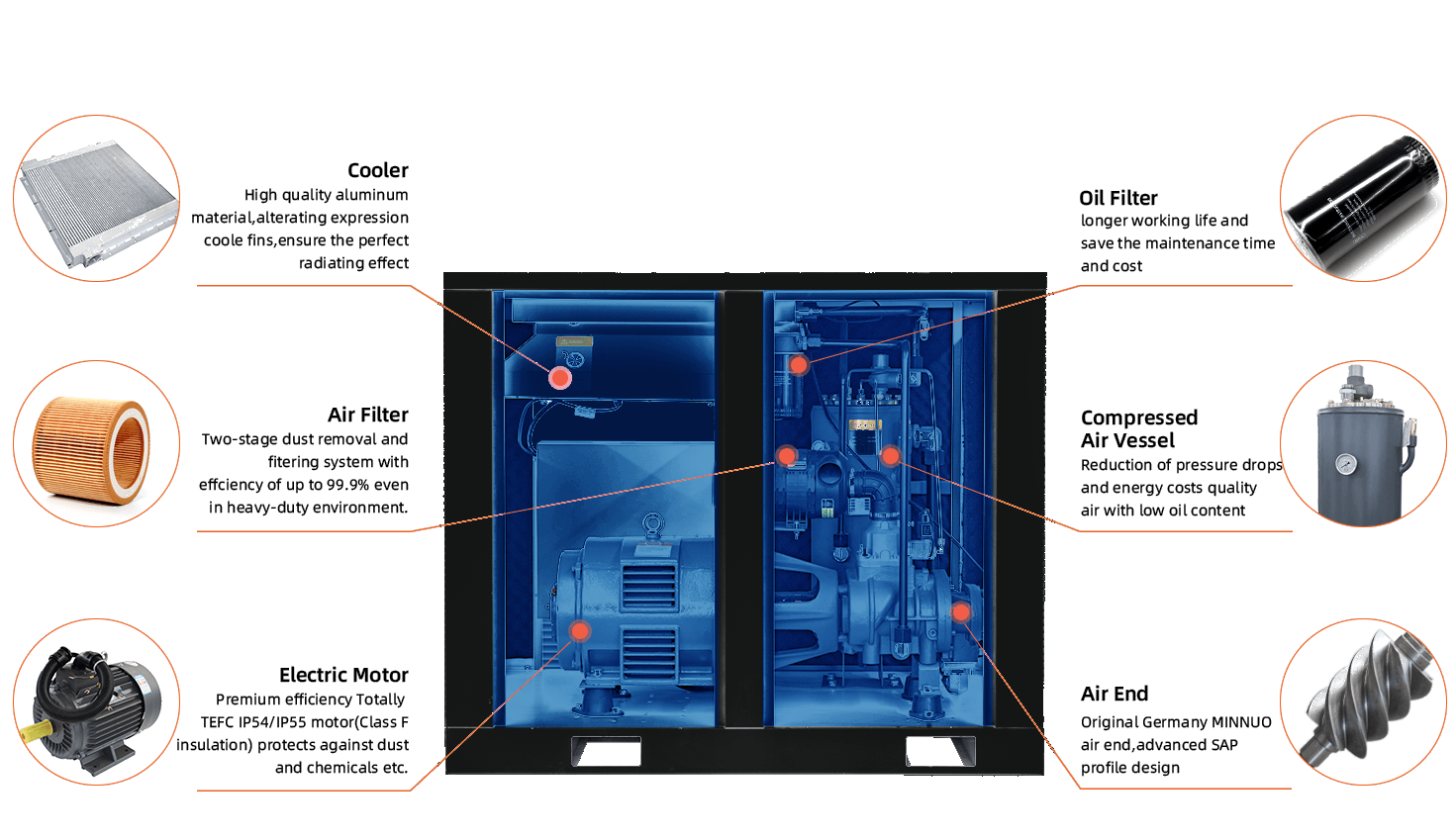
Los compresores industriales son equipos esenciales en sectores como la energía, la química, la metalurgia, la electrónica y el suministro de gases médicos. La elección del tipo de compresor correcto afecta directamente a la eficiencia del sistema, la estabilidad operativa y la seguridad. Este documento describe las principales categorías de compresores y ofrece una guía estructurada para ayudar a los profesionales a seleccionar el más adecuado para sus aplicaciones. 🔧 [...]
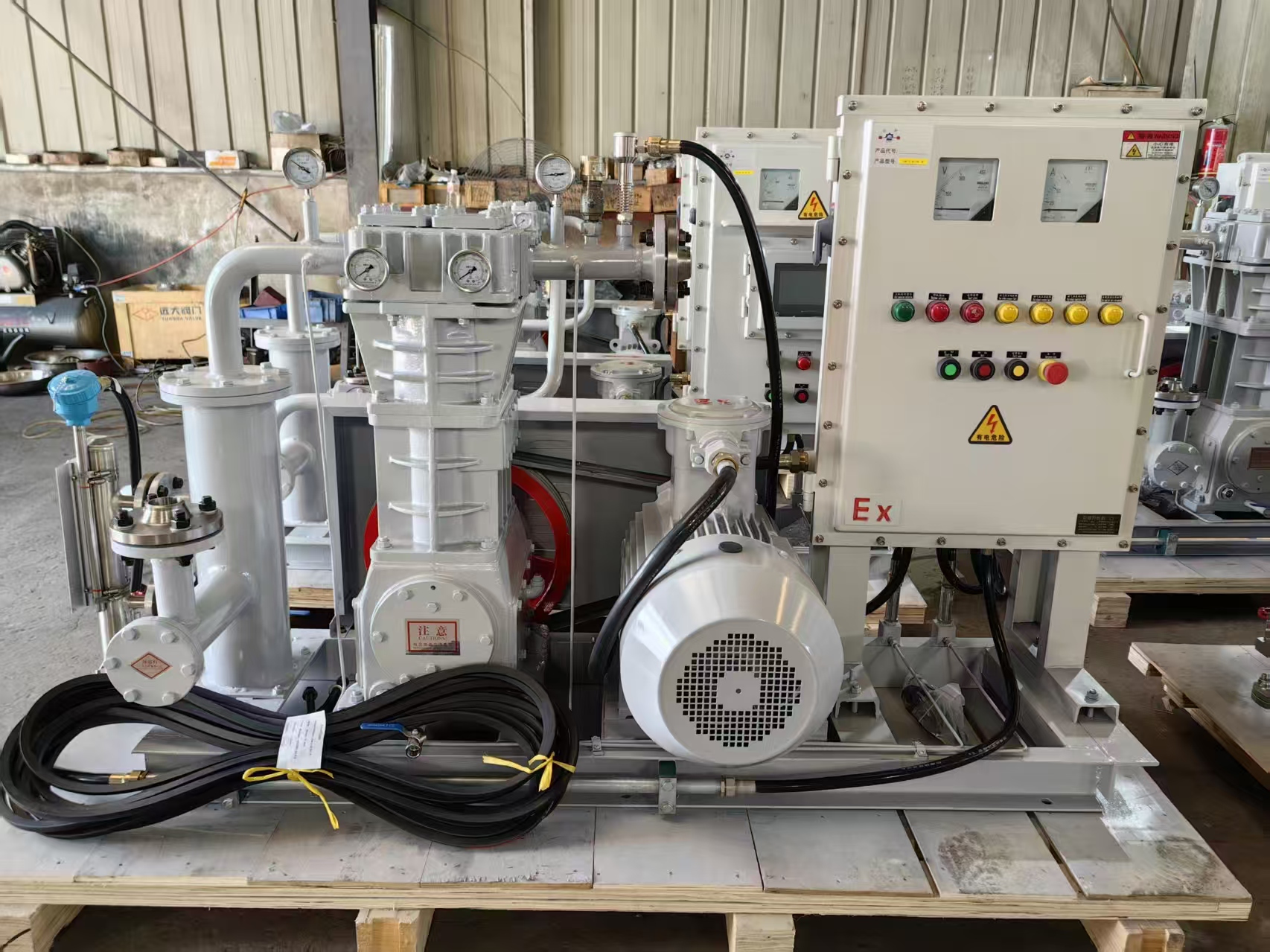
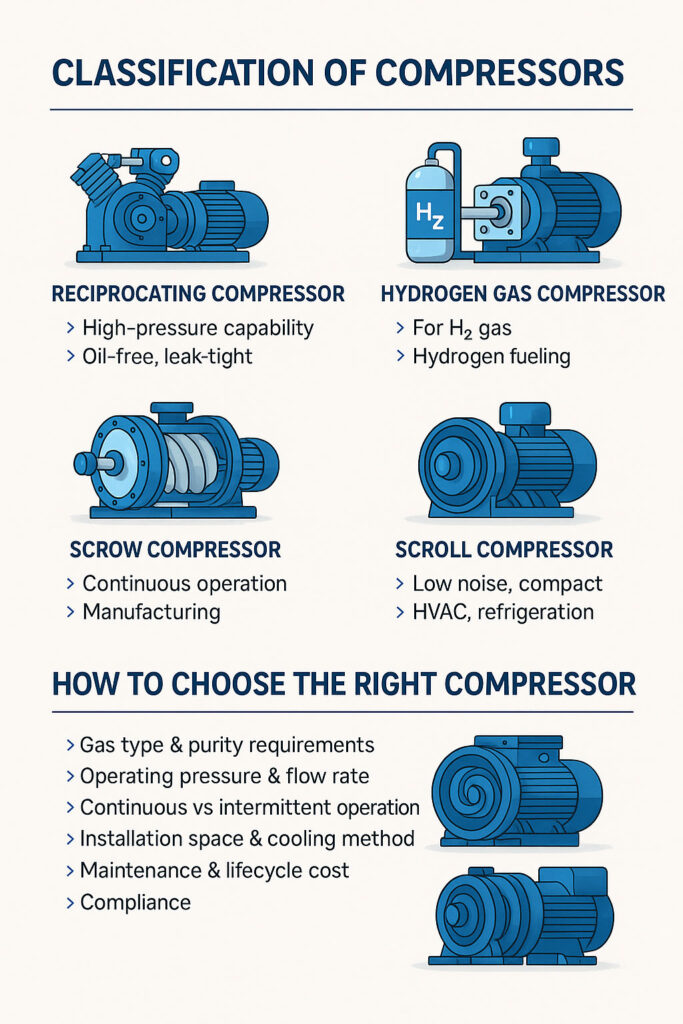
 🔧 1. Compresores alternativos
🔧 1. Compresores alternativos
Visión general:
Los compresores alternativos utilizan pistones accionados por un cigüeñal para suministrar gas a alta presión.
Ventajas:
Capacidad de alta presión
Adecuado para caudales pequeños y medianos
Mantenimiento modular
Lo mejor para:
Plantas petroquímicas, refuerzo del gas natural, estaciones de GNC
💡 2. Compresores de membrana
Visión general:
Se trata de compresores exentos de aceite que utilizan una membrana para aislar el gas de las piezas mecánicas.
Ventajas:
Suministro de gas totalmente exento de aceite
Ideal para gases de alta pureza y peligrosos
Diseño estanco
Lo mejor para:
Compresión de hidrógeno, oxígeno, helio y gases medicinales
⚙️ 3. Compresores de tornillo (compresores rotativos)
Visión general:
Los compresores de tornillo rotativo son máquinas de servicio continuo que comprimen gas mediante dos rotores helicoidales.
Ventajas:
Funcionamiento continuo
Menor vibración
Alta eficiencia para presiones medias
Lo mejor para:
Fabricación, electrónica, metalurgia, herramientas neumáticas
🌀 4. Compresores Scroll
Visión general:
Los compresores scroll utilizan espirales en órbita para comprimir el gas.
Ventajas:
Funcionamiento silencioso
Eficiencia energética
Tamaño compacto
Lo mejor para:
HVAC, refrigeración, laboratorios
💨 5. Compresores centrífugos
Visión general:
Estos compresores dinámicos utilizan impulsores para imprimir velocidad al gas y convertirla en presión.
Ventajas:
Gran capacidad de caudal
Menos piezas móviles
Adecuado para operaciones a gran escala
Lo mejor para:
Plantas de separación de aire, GNL, procesos químicos
🔬 6. Compresores de hidrógeno gaseoso
Visión general:
Unidades especializadas diseñadas para manipular gas hidrógeno ligero y explosivo a alta presión.
Ventajas:
Preferiblemente de diafragma o pistón sin aceite
Altas relaciones de compresión
Excelente estanqueidad y seguridad
Lo mejor para:
Estaciones de abastecimiento de hidrógeno, almacenamiento de energías renovables, producción de amoníaco
⚖️ 7. Scroll vs Tornillo vs Reciprocante: Comparación rápida
| Tipo | Rango de presión | Capacidad de caudal | Mantenimiento | Caso típico |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reciprocante | Alta | Bajo-Medio | Moderado | Gasoducto, GNC |
| Diafragma | Alta | Bajo | Bajo | Gases especiales, laboratorios |
| Tornillo | Medio | Medio-Alto | Bajo | Automatización industrial |
| Desplácese por | Bajo-Medio | Bajo | Bajo | HVAC, refrigeración |
| Centrífuga | Bajo-Medio | Alta | Bajo | GNL, procesos a gran escala |
| Compresores de hidrógeno | Muy alta | Bajo-Medio | Medio-Alto | Energía de hidrógeno, tecnología limpia |
🧭 Cómo elegir el compresor adecuado
Al seleccionar un compresor, tenga en cuenta los siguientes factores:
Tipo de gas y requisitos de pureza (por ejemplo, tóxicos, explosivos, de gran pureza)
Presión de funcionamiento y caudal
Funcionamiento continuo o intermitente
Espacio de instalación y método de refrigeración
Mantenimiento y coste del ciclo de vida
Conformidad (certificaciones CE, ATEX, ISO)









 🔧 1. Compresores alternativos
🔧 1. Compresores alternativos